Hurricane Beryl’s Impact on Jamaica: Hurricane Beryl Jamaica
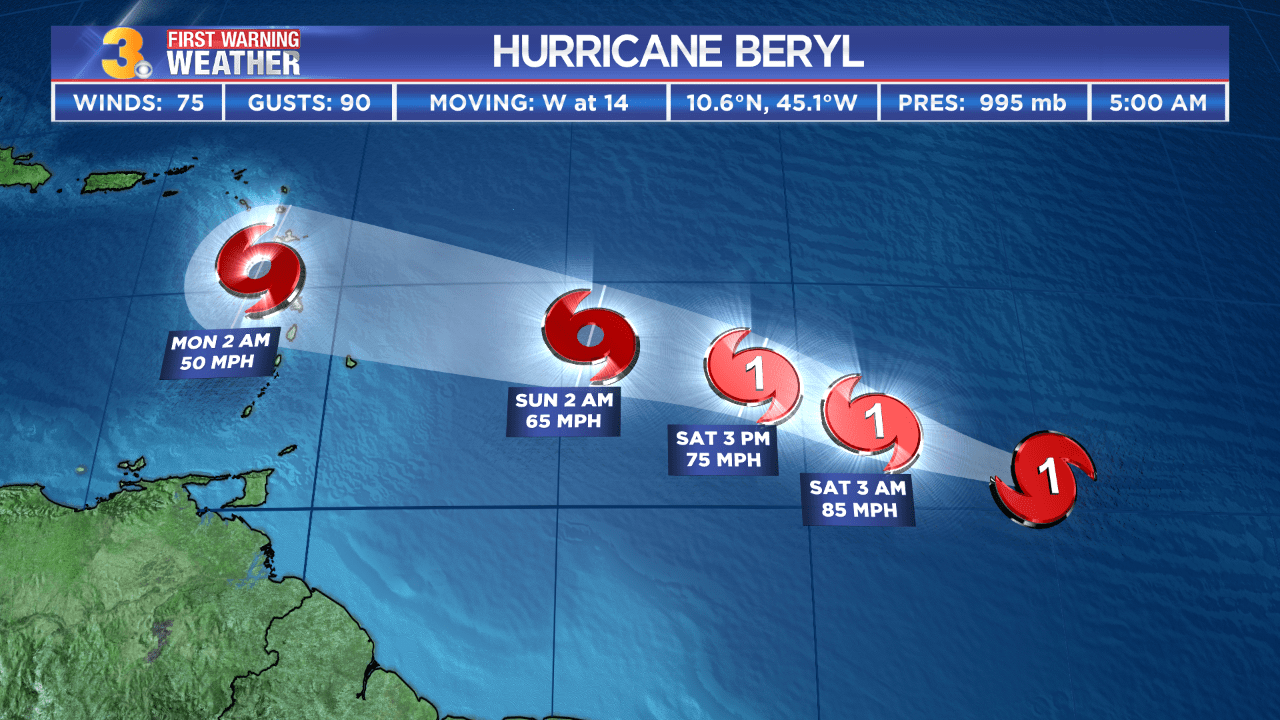
Hurricane beryl jamaica – Hurricane Beryl, a Category 1 hurricane, made landfall in Jamaica on July 5, 2018, bringing with it strong winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surge.
Hurricane Beryl’s Path
Hurricane Beryl approached Jamaica from the southeast, passing over the island’s southern coast near Portland Point. The storm then moved northwest across the island, exiting near Negril on the western coast.
Hurricane Beryl a pass Jamaica, but people deh wonder if it a guh hit Florida. Check will beryl hit florida fi more information. Jamaica did get some rain and wind from Beryl, but no major damage. The storm a expected to weaken as it moves away from the Caribbean.
Wind Speeds, Rainfall, and Storm Surge, Hurricane beryl jamaica
Hurricane Beryl brought sustained winds of up to 120 kilometers per hour (75 miles per hour) to Jamaica. The storm also produced heavy rainfall, with some areas receiving over 200 millimeters (8 inches) of rain. Storm surge of up to 1.5 meters (5 feet) was reported along the southern coast of the island.
Hurricane Beryl a did a wicked ting to Jamaica, but the people dem a did strong and dem did rebuild. Jamaica a did get some serious damage, but the people dem a did come together and dem did help each other out.
Hurricane Beryl Jamaica a did a bad storm, but the people dem a did show dem strength and dem did overcome.
Damage
Hurricane Beryl caused significant damage to Jamaica, particularly in the southern and western regions of the island. Over 1,000 homes were damaged or destroyed, and many businesses were forced to close. The storm also caused widespread power outages and disrupted transportation.
Response and Recovery Efforts
In the face of Hurricane Beryl’s impact, local authorities and aid organizations swiftly mobilized to provide assistance and support.
Evacuation and Shelter Operations
Prior to the storm’s arrival, mandatory evacuations were issued for vulnerable coastal areas. The government coordinated the transportation of residents to designated shelters, which were established in schools, community centers, and other public buildings. These shelters provided essential services such as food, water, and medical assistance.
Debris Removal and Infrastructure Repairs
In the aftermath of the hurricane, extensive debris removal efforts were undertaken to clear roads, restore access to communities, and prevent further damage. Utility crews worked tirelessly to repair damaged power lines, water mains, and other critical infrastructure. The government also allocated funds for long-term infrastructure repairs and upgrades to enhance resilience against future storms.
Financial Assistance
The government provided financial assistance to affected individuals and businesses. This included grants for emergency repairs, loans for rebuilding efforts, and compensation for lost income. International aid organizations also provided financial support to supplement the government’s efforts.
Long-Term Impacts and Lessons Learned
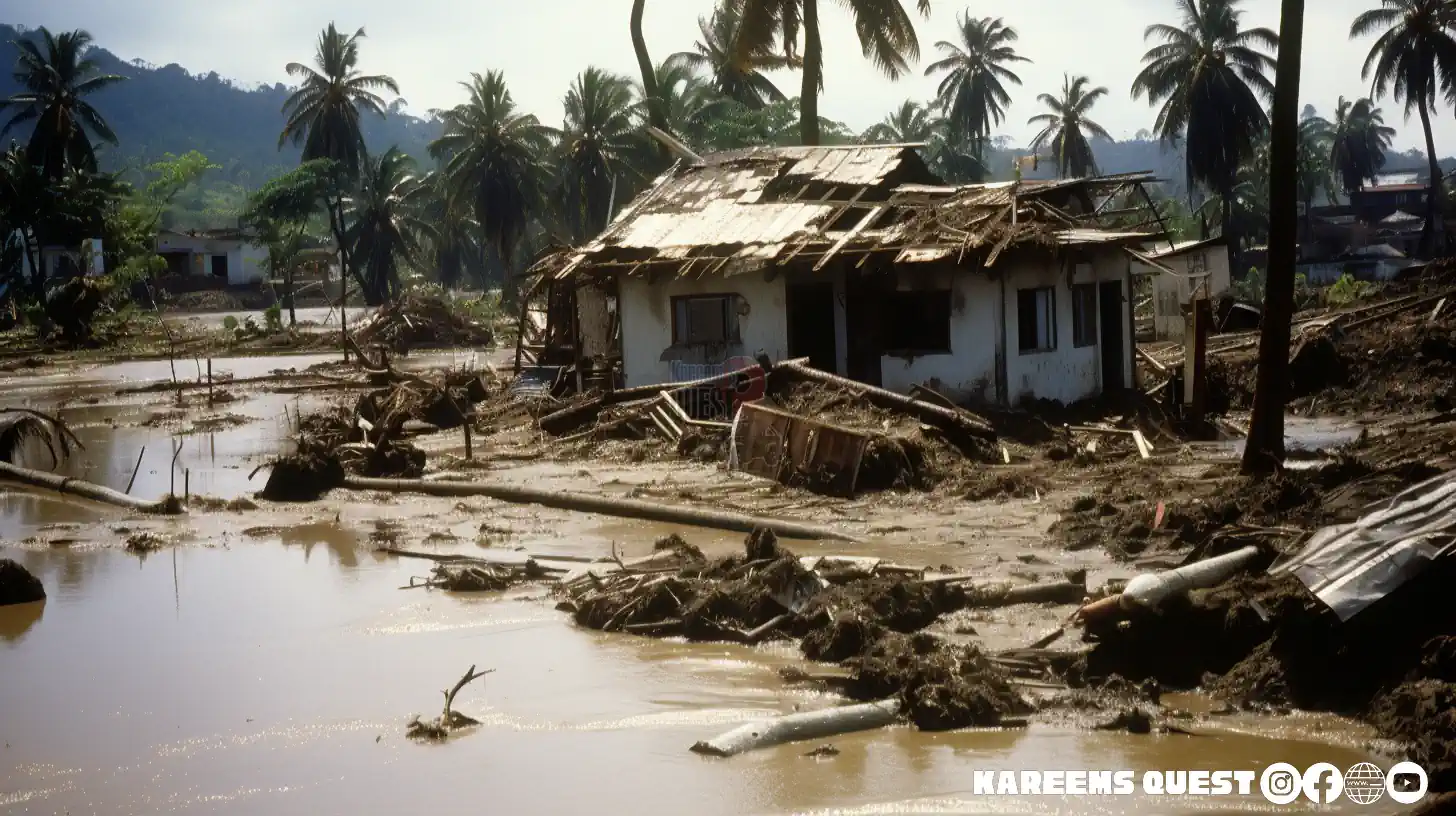

Hurricane Beryl has left a lasting impact on Jamaica, affecting its economy, environment, and society. The storm’s long-term consequences highlight the need for improved disaster preparedness and response plans, as well as strengthening Jamaica’s resilience to future hurricanes.
Economic Impacts
- Infrastructure Damage: Beryl caused widespread damage to homes, businesses, roads, and bridges, disrupting economic activities and livelihoods.
- Tourism Disruption: The tourism industry, a major contributor to Jamaica’s economy, was severely impacted by the storm, leading to a decline in tourist arrivals and revenue.
- Agricultural Losses: The hurricane damaged crops and livestock, resulting in significant losses for farmers and affecting the food supply.
Environmental Impacts
- Coastal Erosion: Beryl’s strong winds and storm surge caused significant coastal erosion, threatening infrastructure and ecosystems.
- Deforestation: The hurricane’s high winds uprooted trees, leading to deforestation and habitat loss for wildlife.
- Pollution: The storm washed away debris and hazardous materials, polluting water sources and coastal areas.
Social Impacts
- Displacement and Homelessness: Many Jamaicans were displaced from their homes due to damage or destruction, creating a housing crisis.
- Health and Safety Concerns: The hurricane disrupted access to clean water, sanitation, and healthcare, increasing the risk of disease outbreaks.
- Psychological Trauma: The storm’s intensity and devastation caused psychological trauma and stress among the affected population.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
The long-term impacts of Hurricane Beryl have highlighted the need for improved disaster preparedness and response plans. Recommendations include:
- Strengthening Building Codes: Revising building codes to ensure structures can withstand future hurricanes.
- Investing in Infrastructure: Upgrading roads, bridges, and other infrastructure to make them more resilient to storms.
- Enhancing Early Warning Systems: Improving weather monitoring and early warning systems to provide timely alerts to communities.
- Promoting Community Resilience: Educating and empowering communities to prepare for and respond to hurricanes.
- Protecting Coastal Ecosystems: Implementing measures to protect coastal ecosystems, such as mangrove restoration and beach nourishment, to mitigate erosion.